7-Day Elimination Diet Meal Plan for Food Sensitivity

What is an Elimination Diet?
This post may contain affiliate links, meaning I may earn a commission if you make a purchase, at no extra cost to you. I only recommend products I trust. Thank you for your support.
An elimination diet is a short-term eating plan designed to help identify foods that might be causing adverse reactions in your body like food sensitivities, intolerances, or allergies.
It works by removing (eliminating) potential trigger foods for a set period (usually 21 days or 2–4 weeks), then gradually reintroducing them one at a time to observe how your body responds.
An elimination diet is often used as a diagnostic tool to pinpoint the cause of digestive issues, skin problems, or other health concerns.
An elimination diet works by;
- Eliminating common food triggers (like dairy, gluten, soy, eggs, nuts, nightshades, etc.).
- Eating a simple, clean diet made of low-allergen, nutrient-rich foods.
- Reintroducing one food group at a time over several days while monitoring for symptoms, after the elimination phase.
- Identifying any foods that trigger reactions like bloating, headaches, fatigue, joint pain, skin issues, or digestive problems.
This 7-day elimination diet for food sensitivity is designed to help you identify and remove common food triggers that may be causing symptoms like bloating, fatigue, headaches, skin issues, and digestive discomfort.
Common Symptoms of Food Sensitivities
These are the common signs and symptoms that an elimination diet can help uncover and improve:
- Bloating or Indigestion: Foods like gluten, dairy, soy, and certain vegetables can trigger bloating by disrupting gut bacteria balance or irritating the intestinal lining.
- Headaches or Migraines: Triggers like processed meats, artificial additives, dairy, gluten, and even histamine-rich foods can inflame blood vessels or affect neurotransmitter function, leading to throbbing headaches, pressure, or migraine attacks.
- Fatigue or Brain Fog: Eating foods your body struggles to tolerate can drain energy, inflame your gut, and disrupt hormones like insulin and cortisol.
- Skin Rashes or Acne: When your gut or immune system reacts to problematic foods, it can manifest externally through skin flare-ups like eczema, hives, rosacea, or acne.
- Joint Pain: Certain food sensitivities contribute to systemic inflammation, which can settle in the joints, causing aches, stiffness, and swelling.
- Mood Swings or Irritability: When your body reacts to irritating foods, it can affect neurotransmitter production (like serotonin and dopamine) and stress hormones, leading to mood fluctuations, anxiety, irritability, or low mood.
7-Day Elimination Diet Meal Plan for Food Sensitivity
This elimination diet for food sensitivity includes low allergen anti-inflammatory foods and excludes common trigger foods such as dairy, eggs, soy, gluten, nuts, seeds, nightshades, or citrus.

Day 1
Breakfast:
- Rice Porridge with Pear: Cook ½ cup white rice in 1 cup water until creamy; top with ½ sliced pear.
Lunch:
- Grilled Turkey Breast with Steamed Zucchini: Grill 4 oz turkey breast; serve with 1 cup steamed zucchini drizzled with 1 tsp olive oil.
Dinner:
- Broiled Salmon with Roasted Broccoli: Broil 4 oz wild‑caught salmon; roast 1 cup broccoli florets with 1 tsp olive oil.
Snacks:
- Baked Pear: Halve and bake 1 pear until tender.
- Carrot Sticks with Olive Oil: 1 cup carrot sticks lightly tossed in 1 tsp olive oil.
Day 2
Breakfast:
- Quinoa Porridge with Apple: Simmer ½ cup quinoa in 1 cup water; top with ½ sliced apple.
Lunch:
- Beef & Kale Stir‑Fry: Sauté 4 oz lean beef strips and 1 cup chopped kale in 1 tsp olive oil until beef is cooked.
Dinner:
- Pork Tenderloin with Roasted Parsnip & Steamed Swiss Chard: Roast a 4 oz pork tenderloin; serve with 1 cup roasted parsnip chunks and 1 cup steamed Swiss chard.
Snacks:
- Cucumber Slices with Olive Oil: 1 cup cucumber rounds, 1 tsp olive oil.
- Sliced Peach: 1 medium peach, sliced.

Day 3
Breakfast:
- Sweet Potato & Pear Hash: Sauté 1 cup diced sweet potato in 1 tsp olive oil until tender; top with ½ cup diced pear.
Lunch:
- Turkey & Spinach Soup: Simmer 4 oz diced turkey breast with 1 cup spinach and 1 cup water; season lightly with sea salt.
Dinner:
- Gochujang Steak, Kimchi & Rice Bowl: Grill 4 oz marinated grass-fed steak; serve over ½ cup cooked white rice with ½ cup napa cabbage slaw.
Snacks:
- Plain Rice Cakes (2 small): Enjoy on their own.
- Steamed Broccoli Florets: 1 cup, no added seasoning.

Day 4
Breakfast:
- Gluten‑Free Oatmeal with Steamed Apple: Cook ½ cup certified gluten‑free oats in 1 cup water; top with ½ cup steamed apple cubes.
Lunch:
- Baked Trout with Sautéed Zucchini & Kale: Bake a 4 oz trout fillet; sauté 1 cup zucchini ribbons and 1 cup chopped kale in 1 tsp olive oil.
Dinner:
- Grilled Chicken with Green Beans & Sweet Potato Mash: Grill 4 oz chicken breast; steam 1 cup green beans; mash one small sweet potato with 1 tsp olive oil.
Snacks:
- Sliced Apple: 1 apple, sliced.
- Cucumber & Parsley Salad: 1 cup cucumber chunks + fresh parsley, tossed with 1 tsp olive oil.

Day 5
Breakfast:
- Brown Rice & Peach Bowl: Stir ½ cup cooked brown rice with ½ cup diced peach.
Lunch:
- Lamb Patties with Steamed Broccoli & Sweet Potato Wedges: Grill two 3 oz lamb patties; steam 1 cup broccoli florets; bake sweet potato wedges from 1 small sweet potato with 1 tsp olive oil.
Dinner:
- Roasted Duck Breast with Steamed Spinach: Roast 4 oz duck breast; serve over 1 cup steamed spinach.
Snacks:
- Zucchini Chips: Thin‑slice 1 zucchini, toss in 1 tsp olive oil, bake until crisp.
- Steamed Spinach: 1 cup, simply steamed.

Day 6
Breakfast:
- Millet Porridge with Stewed Pear: Cook ½ cup millet in 1 cup water; top with ½ cup stewed pear.
Lunch:
- Turkey Lettuce Wraps: Sauté 4 oz ground turkey; wrap in 4 butter lettuce leaves.
Dinner:
- Turkey & Butternut Squash Bone Broth Soup: Simmer 3 oz diced turkey breast in 1 cup chicken bone broth with 1 cup peeled, diced butternut squash until squash is soft.
Snacks:
- Steamed Cauliflower Florets: 1 cup, plain.
- Rice Pudding: Simmer ½ cup cooked rice in ½ cup water until thick and creamy.

Day 7
Breakfast:
- Buckwheat Porridge with Pear: Cook ½ cup hulled buckwheat in 1 cup water; top with ½ cup diced pear.
Lunch:
- Beef Meatballs with Zucchini Noodles: Bake two 3‑oz beef meatballs; serve over 1 cup spiralized zucchini.
Dinner:
- Lamb & Kale Bone Broth Soup: Simmer 3 oz cubed lamb shoulder in 1 cup beef bone broth with 1 cup chopped kale and 1 clove minced garlic until kale softens.
Snacks:
- Cucumber Spears: 1 cup, plain.
- Steamed Sweet Potato Cubes: 1 cup, simply steamed.
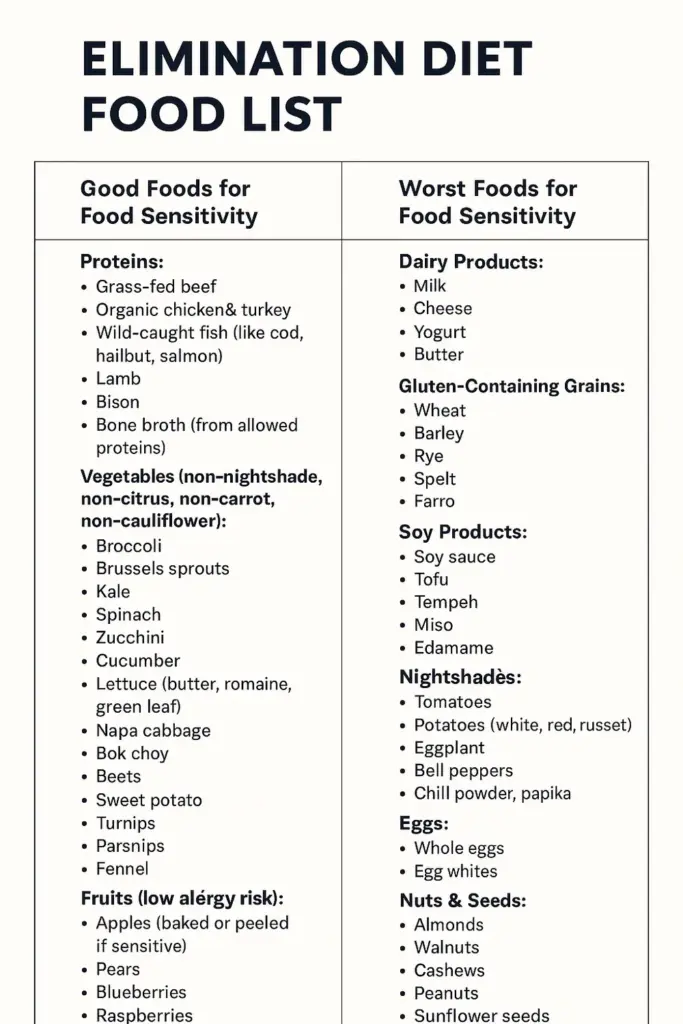
Good Foods for Food Sensitivity
These foods are generally well tolerated and can be included in an elimination diet food list:
1. Proteins
- Grass-fed beef
- Organic chicken & turkey
- Wild-caught fish (like cod, halibut, salmon)
- Lamb
- Bison
- Bone broth (from allowed proteins)
2. Non-Nightshade Vegetables
- Broccoli
- Brussels sprouts
- Kale
- Spinach
- Zucchini
- Cucumber
- Lettuce (butter, romaine, green leaf)
- Napa cabbage
- Bok choy
- Beets
- Sweet potato
- Turnips
- Parsnips
- Fennel
3. Fruits (Low Allergy Risk)
- Apples (baked or peeled if sensitive)
- Pears
- Blueberries
- Raspberries
- Watermelon
- Mango (if tolerated)
- Papaya
4. Gluten-Free Grains & Starches
- White rice
- Quinoa (if tolerated)
- Cassava
- Sweet potato
- Plantains
5. Healthy Fats
- Olive oil
- Avocado oil (highly refined)
- Coconut oil (if tolerated)
6. Herbs & Flavorings
- Fresh parsley
- Basil
- Dill
- Ginger
- Turmeric
- Coconut aminos (soy-free alternative to soy sauce)
- Apple cider vinegar (if tolerated)
7. Beverages
- Filtered water
- Herbal teas (ginger, peppermint, chamomile — no citrus or additives)
- Bone broth (from allowed proteins)
Worst Foods for Food Sensitivity
These foods are common triggers and can lead to symptoms such as bloating, headaches, fatigue, skin issues, and digestive discomfort:
1. Dairy Products
- Milk
- Cheese
- Yogurt
- Butter
2. Gluten-Containing Grains
- Wheat
- Barley
- Rye
- Spelt
- Farro
3. Soy Products
- Soy sauce
- Tofu
- Tempeh
- Miso
- Edamame
4. Nightshades
- Tomatoes
- Potatoes (white, red, russet)
- Eggplant
- Bell peppers
- Hot peppers
- Chili powder, paprika
5. Eggs
- Whole eggs
- Egg whites
6. Nuts & Seeds
- Almonds
- Walnuts
- Cashews
- Peanuts
- Sunflower seeds
- Chia seeds
- Flaxseeds
7. Citrus Fruits
- Oranges
- Lemons
- Limes
- Grapefruit
8. Corn & Corn Derivatives
- Cornmeal
- Corn syrup
- Corn oil
- Popcorn
9. Processed & Packaged Foods
- Chips
- Packaged snacks
- Deli meats
- Canned soups (unless clean, elimination-friendly)
10. Artificial Additives
- MSG
- Artificial sweeteners (aspartame, sucralose)
- Artificial colors and flavors
11. Legumes
- Beans (black, kidney, pinto)
- Lentils
- Peas
12. Others
- Carrots (can be a hidden trigger)
- Cauliflower (can cause bloating for some)
- Vinegar (except apple cider vinegar in small amounts if tolerated)
Benefits of an Elimination Diet
Here are some of the key benefits of following an elimination diet:
- Identifies Trigger Foods: Helps pinpoint specific foods that cause symptoms like bloating, headaches, skin issues, or joint pain by systematically removing and reintroducing them.
- Reduces Chronic Inflammation: By avoiding reactive foods, the body calms its inflammatory response, which may help with joint pain, skin flare-ups, digestive problems, and fatigue.
- Improves Digestive Health: Eliminating common irritants like gluten, dairy, soy, and nightshades can ease symptoms like gas, bloating, diarrhea, constipation, and acid reflux.
- Eases Skin Conditions: Many people see improvement in eczema, acne, psoriasis, and rosacea when food triggers are removed and gut health improves.
- Boosts Energy Levels: Chronic food sensitivities can quietly drain energy. Removing problem foods often leads to steadier, more sustained daily energy.
- Enhances Mental Clarity: Food sensitivities are linked to brain fog, mood swings, and anxiety. An elimination diet can sharpen focus and promote a more balanced mood.
- Supports Gut Healing: Without inflammatory foods, the gut lining has a chance to repair, reducing issues like leaky gut and improving overall nutrient absorption.
- Promotes Weight Balance: Some food sensitivities can contribute to water retention and weight fluctuations. Elimination diets help regulate these effects naturally.
- Strengthens Immune Function: Lowering inflammation and irritation in the gut reduces strain on the immune system, supporting better overall immunity.
- Reduces Migraines & Headaches: Common trigger foods like gluten, dairy, and artificial additives are often culprits in chronic headaches and migraines, removing them may bring relief.
Final Thoughts
An elimination diet is one of the most effective tools for uncovering hidden food sensitivities and understanding how your body responds to the foods you eat every day.
By removing common trigger foods and mindfully reintroducing them, you can identify the culprits behind symptoms like bloating, headaches, skin issues, fatigue, and mood swings.
The elimination diet for food sensitivity is not just about restriction, it’s about gaining clarity, healing your gut, reducing inflammation, and reclaiming your energy and well-being.
While the process takes a bit of patience and attention to detail, the long-term benefits of eating in alignment with your body’s needs are well worth it.
The significance of undertaking such a diet under professional guidance cannot be overstated, as it ensures both safety and effectiveness in the quest to achieve optimal health.
If you’re struggling with unexplained symptoms or suspect certain foods may be affecting your health, an elimination diet, guided by a healthcare professional can be a powerful way to reset your system and rediscover what makes you feel your best.
- 7-day meal plan for pregnant women
- High protein diet plan
- 3000 calorie meal plan for muscle gain
- 7-day PCOS diet meal plan
- How to remove PCOS belly fat forever
- Menopause diet plan to lose weight
- The 90-30-50 diet plan
- 7-day meal plan for gestational diabetes
- 7-day meal plan for high blood pressure
- 7-day carb cycling meal plan
- How long does it take to reverse prediabetes?
- 30-day low fodmap meal plan
- 21-day fatty liver diet plan
- Vegetarian breakfast ideas
- Benefits of green bananas
- What is chicken meal in dog food?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does an elimination diet work?
An elimination diet works by removing common trigger foods like dairy, gluten, soy, eggs, nuts, and processed foods.
After a set period, these foods are reintroduced individually to help identify which ones cause symptoms such as bloating, headaches, or skin issues.
How long should you follow an elimination diet?
Most elimination diets last for 2 to 4 weeks, followed by a structured reintroduction phase where eliminated foods are added back in one at a time every 3–5 days while monitoring for reactions.
Are food sensitivity tests accurate?
At-home tests (IgG tests) are controversial, elimination diets are considered the gold standard for identifying sensitivities.
Can an elimination diet help with IBS?
Yes, studies show elimination diets (like the low-FODMAP diet) can reduce IBS symptoms by identifying trigger foods like lactose or gluten.
Which foods are usually eliminated first?
Common culprits include dairy, gluten, soy, eggs, nuts, corn, nightshades (tomatoes, peppers), and processed foods.




