What is Electrotherapy: 10 Proven Key Benefits Revealed
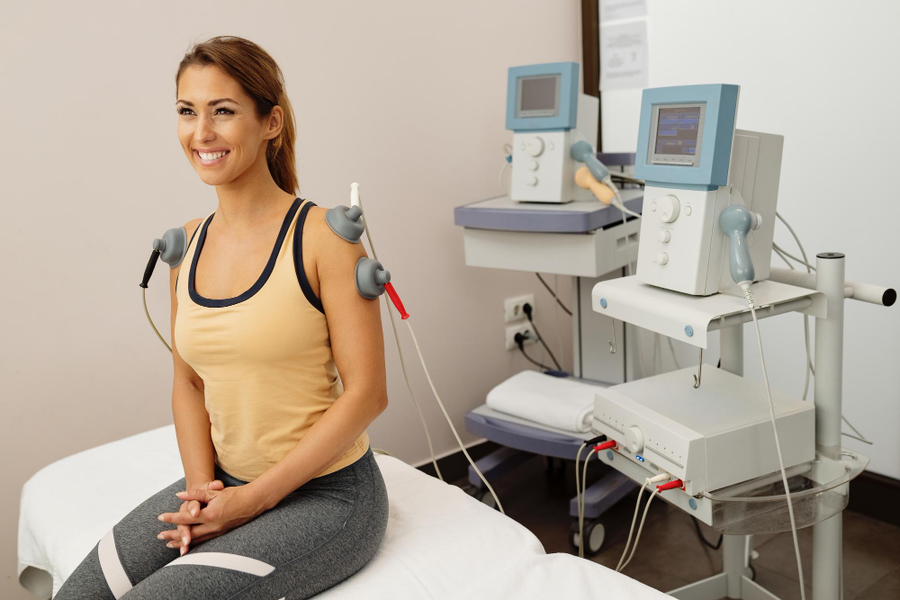

- What is Electrotherapy and How Does It Work?
- 10 Proven Key Benefits of Electrotherapy for Pain Relief
- Electrotherapy Devices and Their Features
- Different Types of Electrotherapy Stimulation
- How to Use Electrotherapy for Specific Conditions
- Precautions and Safety Measures for Electrotherapy
- Electrotherapy vs Other Pain Relief Methods
- Credible References and Resources About Electrotherapy’s Effectiveness
- Conclusion: The Future of Electrotherapy in Pain Management and Healing
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Electrotherapy and How Does It Work?
This post may contain affiliate links, meaning I may earn a commission if you make a purchase, at no extra cost to you. I only recommend products I trust. Thank you for your support.
Electrotherapy is a non-invasive treatment method that utilizes electrical currents to specific areas of the body. to provide pain relief and promote healing.
These currents stimulate the nerves and muscles, producing a range of therapeutic effects.
It has been used for decades in various medical fields, including sports medicine, physical therapy, and chiropractic care.
By understanding what electrotherapy is and how it works, you can discover its immense benefits for pain management and recovery.
Here are the different types of electrotherapy and how they work:
1. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS):
TENS is one of the most common type of electrotherapy. It involves placing electrode pads on the skin near the affected area.
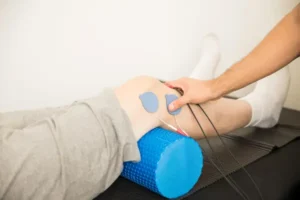
The electrical impulses generated by the TENS unit help to block pain signals from reaching the brain, providing temporary pain relief.
2. Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS):
EMS is another type of electrotherapy that focuses on stimulating muscles by delivering electrical currents directly to the muscles.
EMS can help increase blood flow, reduce muscle spasms, and improve muscle strength and tone.
3. Interferential Current Therapy (IFT):
IFT involves the use of two medium-frequency electrical currents that intersect and penetrate deep into the tissues.
This type is particularly effective for relieving pain, reducing inflammation, and promoting tissue healing.
4. Cranial Electrotherapy Stimulation (CES):
CES involves the application of low-level electrical currents to the cranium, specifically targeting the brain by delivering intermittent bursts of gentle electrical impulses.
This unique form of stimulation has shown promise in various applications, potentially aiding in stress reduction, anxiety management, and improved sleep patterns.
CES offers a non-invasive approach to addressing certain mental health and wellness concerns through its targeted electrical intervention.
10 Proven Key Benefits of Electrotherapy for Pain Relief
Electrotherapy offers numerous benefits for pain relief, making it a popular choice among healthcare professionals.
These include:
1. Drug-Free Pain Relief:
- Electrotherapy provides a non-pharmacological approach to pain management, reducing the need for medications and their associated side effects.
2. Increased Circulation:
- Electrical currents stimulate blood flow, which delivers oxygen and nutrients to the affected area, promoting healing and reducing inflammation.
3. Muscle Relaxation:
- Electrotherapy helps to relax muscles, relieve muscle spasms, and reduce muscle tension, ultimately alleviating pain and improving flexibility.
4. Enhanced Endorphin Release:
- The electrical stimulation triggers the release of endorphins, the body’s natural painkillers, providing long-lasting pain relief.
5. Improved Range of Motion:
- By reducing pain and inflammation and increasing muscle flexibility, electrotherapy can enhance joint mobility and overall range of motion.
6. Accelerated Healing:
- The electrical currents stimulate cell regeneration and tissue repair, speeding up the healing process for acute and chronic injuries.
7. Versatility:
- Electrotherapy can be used to treat various conditions, including musculoskeletal injuries, neuropathic pain, arthritis, and sports-related injuries.
8. Easy to Use:
- Electrotherapy devices are user-friendly and can be used at home, allowing individuals to manage their pain and recovery conveniently.
9. Cost-Effective:
- It provides a cost-effective alternative to more invasive and expensive treatment options, such as surgery.
10. Non-Addictive:
- Unlike certain pain medications, electrotherapy is non-addictive and poses no risk of dependency or withdrawal symptoms.
Electrotherapy Devices and Their Features
When it comes to electrotherapy, there is a wide range of devices available, each with its unique features and benefits.
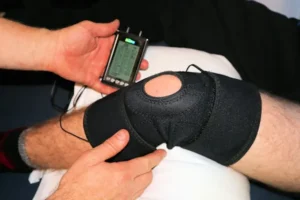
Here are ten popular devices on the market:
1. TENS Units:
- TENS units are portable devices that deliver low-voltage electrical currents through electrode pads.
- They offer various intensity settings and pre-programmed modes for targeted pain relief.
2. EMS Devices:
- EMS devices are designed to stimulate muscles and improve strength and tone.
- They typically feature adjustable intensity levels and customizable programs for different muscle groups.
3. IFT Machines:
- Interferential Current Therapy machines utilize medium-frequency currents for deep tissue stimulation.
- They often come with multiple electrode channels and pre-set treatment programs.
4. Ultrasound Units:
- Ultrasound devices use sound waves to generate deep heating in the tissues.
- They are commonly used for pain relief, reducing inflammation, and promoting tissue healing.
5. Microcurrent Devices:
- Microcurrent devices deliver extremely low-intensity electrical currents.
- They are particularly effective for promoting cellular healing and reducing inflammation.
6. High-Frequency Therapy Devices:
- High-frequency therapy devices utilize high-frequency currents to provide pain relief and improve blood circulation.
- They are often used for chronic pain conditions.
7. Russian Muscle Stimulators:
- Russian muscle stimulators are specifically designed for muscle strengthening and rehabilitation.
- They produce a strong but comfortable current to activate muscles.
8. Iontophoresis Machines:
- Iontophoresis machines use electrical currents to deliver medication through the skin.
- They are commonly used for conditions such as hyperhidrosis and localized pain relief.
9. Spinal Cord Stimulators:
- Spinal cord stimulators are implantable devices that deliver electrical currents directly to the spinal cord.
- They are used for chronic pain management when other methods have failed.
10. Combination Therapy Devices:
- Combination therapy devices combine different forms of electrotherapy, such as TENS and EMS, in a single unit.
- They offer versatile treatment options for various conditions.
Each of these devices has its own set of features and benefits, so it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine which device is most suitable for your specific needs.
Different Types of Electrotherapy Stimulation
Electrotherapy stimulation comes in various forms, each targeting specific therapeutic effects.
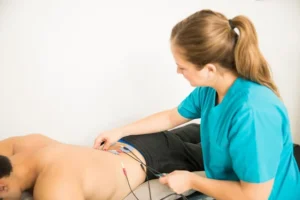
By understanding the different types of stimulation, you can choose the most appropriate method for your pain relief and healing needs.
Here are the most common types of electrotherapy stimulation:
1. Continuous Stimulation:
- Continuous stimulation involves the constant delivery of electrical currents to the affected area.
- It is often used for chronic pain management and promoting long-term healing.
2. Burst Stimulation:
- Burst stimulation delivers intermittent bursts of electrical currents.
- This type of stimulation can help manage acute pain and muscle spasms effectively.
3. Modulated Stimulation:
- Modulated stimulation involves the variation of electrical parameters, such as frequency and intensity, over time.
- It helps prevent accommodation and ensures optimal pain relief.
4. Symmetrical Biphasic Stimulation:
- Symmetrical biphasic stimulation delivers equal electrical currents in both directions.
- It is commonly used for muscle stimulation and pain relief.
5. Asymmetrical Biphasic Stimulation:
- Asymmetrical biphasic stimulation delivers electrical currents that differ in shape and duration.
- It can be used for various therapeutic purposes, including pain relief and muscle rehabilitation.
6. Rectangular Stimulation:
- Rectangular stimulation delivers square-wave electrical currents.
- This type of stimulation is often used for sensory nerve stimulation and pain relief.
7. Triangular Stimulation:
- Triangular stimulation delivers triangular-shaped electrical currents.
- It is commonly used for muscle stimulation and rehabilitation.
8. Russian Stimulation:
- Russian stimulation delivers bursts of electrical currents at a frequency of 2,500 Hz.
- It is particularly effective for muscle strengthening and toning.
9. Low-Frequency Stimulation:
- Low-frequency stimulation typically refers to electrical currents with frequencies below 1,000 Hz.
- It is often used for pain relief and muscle relaxation.
10. High-Frequency Stimulation:
- High-frequency stimulation refers to electrical currents with frequencies above 1,000 Hz.
- It is commonly used for sensory nerve stimulation and pain relief.
By understanding the different types of electrotherapy stimulation, you can work with your healthcare professional to determine the most suitable method for your specific condition and treatment goals.
How to Use Electrotherapy for Specific Conditions
Electrotherapy can be used to treat a wide range of conditions, providing targeted pain relief and promoting healing.
Here’s how electrotherapy can be used for specific conditions:
1. Musculoskeletal Injuries:
- For sprains, strains, and other musculoskeletal injuries, TENS units can be used to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
- EMS devices can also be beneficial for muscle rehabilitation and strengthening.
2. Arthritis:
- TENS units and IFT machines can provide pain relief and improve joint mobility for individuals with arthritis.
- Low-frequency stimulation is often effective for reducing arthritic pain.
3. Neuropathic Pain:
- TENS units are commonly used to manage neuropathic pain.
- By blocking pain signals, TENS can provide significant relief for individuals with conditions such as diabetic neuropathy or sciatica.
4. Sports Injuries:
- Electrotherapy can play a crucial role in sports injury rehabilitation.
- EMS devices help to strengthen weakened muscles, while ultrasound therapy can aid in tissue healing.
5. Post-Surgical Recovery:
- It can enhance post-surgical recovery by reducing pain, promoting blood circulation, and accelerating tissue healing.
- TENS units and IFT machines are often used in this context.
6. Fibromyalgia:
- TENS units and IFT machines can be effective in managing the pain associated with fibromyalgia.
- By stimulating the nerves and promoting endorphin release, electrotherapy can provide relief.
7. Chronic Pain Conditions:
- Electrotherapy, particularly TENS units, can be used as a non-pharmacological approach for managing chronic pain conditions such as back pain, migraines, and fibromyalgia.
8. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome:
- TENS units and Iontophoresis machines can be used to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation associated with carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Electrotherapy can provide temporary relief while other treatments are pursued.
9. Plantar Fasciitis:
- Ultrasound therapy can be effective in reducing pain and promoting healing for individuals with plantar fasciitis.
- It helps to alleviate inflammation and stimulate tissue repair.
10. Post-Stroke Rehabilitation:
- Electrotherapy can aid in post-stroke rehabilitation by stimulating weakened muscles, improving range of motion, and promoting neuroplasticity.
- EMS devices are commonly utilized in this context.
It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate electrotherapy approach for your specific condition and treatment plan.
Precautions and Safety Measures for Electrotherapy
While electrotherapy is generally safe and well-tolerated, it’s essential to follow certain precautions and safety measures to ensure optimal results and minimize the risk of adverse effects.
These are some key precautions to consider:
1. Consult with a Healthcare Professional:
Before starting any electrotherapy treatment, consult with a healthcare professional to determine if it is suitable for your specific condition and overall health.
2. Follow Instructions:
Carefully read and follow the instructions provided with your device. Pay attention to the recommended treatment duration, intensity levels, and electrode placement.
3. Proper Electrode Placement:
Ensure that the electrode pads are placed correctly on the skin, following the guidance provided with your device. Incorrect placement may result in ineffective treatment or discomfort.
4. Skin Preparation:
Cleanse the skin thoroughly before applying the electrode pads. Remove any oil, lotion, or sweat to ensure optimal electrode adherence and electrical conductivity.
5. Avoid Open Wounds or Broken Skin:
Do not apply electrotherapy to areas with open wounds, broken skin, or infections. It should be used only on intact skin.
6. Sensitivity and Allergies:
If you have sensitive skin or a known allergy to adhesives, consider using hypoallergenic electrode pads or consult with a healthcare professional for alternative options.
7. Adjust Intensity Gradually:
When using electrotherapy for the first time or after a prolonged break, start with the lowest intensity setting and gradually increase it to a comfortable level.
This allows your body to adjust to the electrical stimulation.
8. Sensations:
During electrotherapy, you may experience various sensations, including tingling, warmth, or mild muscle contractions.
These sensations are normal, but if you experience sharp pain or discomfort, adjust the intensity or contact your healthcare professional.
9. Pregnant Women:
Pregnant women should exercise caution when using electrotherapy. Consult with a healthcare professional or obstetrician before proceeding with any treatment.
10. Medical Implants:
Individuals with medical implants, such as pacemakers or defibrillators, should avoid using electrotherapy devices unless explicitly cleared by their healthcare professional.
Electrotherapy vs Other Pain Relief Methods
When it comes to pain relief, electrotherapy offers distinct advantages over other methods.
Here’s a brief comparison:
| Electrotherapy | Medications | Surgery | Physical Therapy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-invasive and drug-free | Relies on medications, which may cause side effects | Invasive and involves potential risks and recovery time | Non-invasive and focuses on manual techniques and exercises |
| Provides targeted pain relief and promotes healing | Provides temporary pain relief without addressing the underlying cause | Treats the underlying cause but may have limitations and risks | Aims to improve mobility, strength, and function |
| Can be used at home for convenient pain management | Requires a prescription and regular refills | Requires hospitalization and specialized medical facilities | Requires regular visits to a therapist or rehabilitation center |
| Wide range of devices and stimulation options for personalized treatment | Limited options and may not be suitable for everyone | Case-specific and depends on the individual’s condition | Tailored to the individual’s needs and progress |
| Offers versatile treatment options for various conditions | May not address the root cause of the pain | May be the only option for certain conditions or injuries | Complements other pain relief methods and aids in rehabilitation |
It’s important to note that the choice of pain relief method depends on the individual’s condition, preferences, and recommendations from healthcare professionals.
In some cases, a combination of different approaches may be the most effective solution.
Credible References and Resources About Electrotherapy’s Effectiveness
To further support the effectiveness and credibility of electrotherapy, let’s explore some reputable references and resources:
1. The Use of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) in Pain Relief in individuals with knee osteoarthritis:
A comprehensive study published in the Wiley Online Library. The study analyzes the efficacy of TENS units in reducing pain and improving quality of life.
The research reveals significant evidence of immediate pain relief in individuals with mild-to-moderate knee osteoarthritis.
2. Electrical Stimulation Therapy to Enhance Wound Healing:
This study published in the National Library of Medicine examines the benefits of electrical stimulation therapy in wound healing.
The study provides insights into the mechanisms behind electrotherapy’s positive impact on wound healing.
3. Evidence Review for Electrical Physical Modalities for Chronic Primary Pain:
A comprehensive review published in the the National Library of Medicine, exploring the various electrotherapy techniques used in chronic pain management.
The review provides a detailed analysis of the evidence benefits and limitations of electrotherapy in chronic pain relief.
4. Comparative Study of Different Electrotherapy Methods for Pain Management in Knee Osteoarthritis:
A comparative study published in the the International Journal of Physical Therapy, comparing the effectiveness of various electrotherapy methods in managing pain caused by knee osteoarthritis.
The study provides valuable insights for healthcare professionals and patients seeking alternative pain management options.
Conclusion: The Future of Electrotherapy in Pain Management and Healing
As we have explored in this article, electrotherapy holds immense potential as a cutting-edge treatment option for rapid pain relief and enhanced healing.
Its ability to alleviate pain, promote healing, and rehabilitate muscles has made it a valuable tool in various healthcare settings.
With the continuous advancements in technology, we can expect electrotherapy devices to become more sophisticated, user-friendly, and tailored to individual needs.
As healthcare professionals and patients realize the benefits and effectiveness of electrotherapy, the future of this innovative technique in pain management and healing looks promising.
Consider reading these insightful articles covering diverse strategies for pain relief and management: Physical therapist salary, Benefits of physical therapy, hip fracture recovery strategies, best assistive devices for elderly, moringa benefits in pain management, and effectiveness of botox therapy for chronic migraines.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is electrotherapy safe?
Yes, electrotherapy is generally safe when used as directed by healthcare professionals.
However, it may not be suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions or those who have implanted medical devices.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before undergoing electrotherapy.
How long does an electrotherapy session last?
The duration of an electrotherapy session can vary depending on the specific treatment and the individual’s condition.
Sessions typically range from 15 minutes to an hour, with multiple sessions recommended for optimal results.
Are there any side effects of electrotherapy?
While rare, some individuals may experience mild side effects such as skin irritation, tingling sensations, or muscle twitching.
These side effects are usually temporary and subside shortly after the treatment.
Can I use electrotherapy at home?
Yes, there are portable electrotherapy devices available for home use. However, it is important to receive proper guidance from a healthcare professional to ensure safe and effective use.
Does insurance cover electrotherapy treatments?
Insurance coverage for electrotherapy treatments may vary depending on the provider and the specific policy.
It is advisable to check with your insurance company to determine coverage options.
Now that you have gained a comprehensive understanding of electrotherapy, its benefits, and its future potential, you can make an informed decision about incorporating this innovative treatment option into your pain management and healing journey.
Take the first step towards a healthier, pain-free life by exploring the possibilities of electrotherapy today.